
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Complications
- Therapeutic Effects of Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 on Diabetic Nephropathy and the Possible Mechanism in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Mice
- Wenya Weng, Tingwen Ge, Yi Wang, Lulu He, Tinghao Liu, Wanning Wang, Zongyu Zheng, Lechu Yu, Chi Zhang, Xuemian Lu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):566-580. Published online May 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0089
- 5,919 View
- 102 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
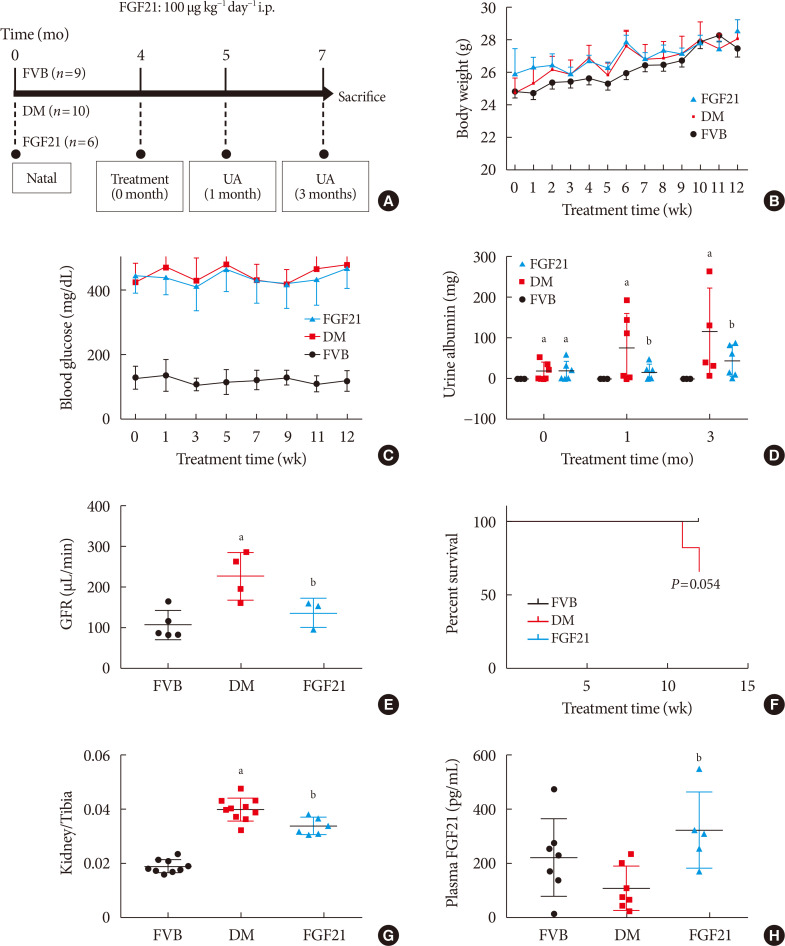
ePub Background Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) has been only reported to prevent type 1 diabetic nephropathy (DN) in the streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) mouse model. However, the FVB (Cg)-Tg (Cryaa-Tag, Ins2-CALM1) 26OVE/PneJ (OVE26) transgenic mouse is a widely recommended mouse model to recapture the most important features of T1DM nephropathy that often occurs in diabetic patients. In addition, most previous studies focused on exploring the preventive effect of FGF21 on the development of DN. However, in clinic, development of therapeutic strategy has much more realistic value compared with preventive strategy since the onset time of DN is difficult to be accurately predicted. Therefore, in the present study OVE26 mice were used to investigate the potential therapeutic effects of FGF21 on DN.
Methods Four-month-old female OVE26 mice were intraperitoneally treated with recombinant FGF21 at a dose of 100 µg/kg/day for 3 months. The diabetic and non-diabetic control mice were treated with phosphate-buffered saline at the same volume. Renal functions, pathological changes, inflammation, apoptosis, oxidative stress and fibrosis were examined in mice of all groups.
Results The results showed that severe renal dysfunction, morphological changes, inflammation, apoptosis, and fibrosis were observed in OVE26 mice. However, all the renal abnormalities above in OVE26 mice were significantly attenuated by 3-month FGF21 treatment associated with improvement of renal adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity and sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) expression.
Conclusion Therefore, this study demonstrated that FGF21 might exert therapeutic effects on DN through AMPK-SIRT1 pathway.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fibroblast growth factor 21 alleviates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
Wenhui Zhong, Yuheng Jiang, Huizhen Wang, Xiang Luo, Tao Zeng, Huimi Huang, Ling Xiao, Nan Jia, Aiqing Li
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2024; 1871(2): 119620. CrossRef - Urinary Excretion of Biomolecules Related to Cell Cycle, Proliferation, and Autophagy in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
Anton I. Korbut, Vyacheslav V. Romanov, Vadim V. Klimontov
Biomedicines.2024; 12(3): 487. CrossRef - New developments in the biology of fibroblast growth factors
David M. Ornitz, Nobuyuki Itoh
WIREs Mechanisms of Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - SIRT1–SIRT7 in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
Wenxiu Qi, Cheng Hu, Daqing Zhao, Xiangyan Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Fibrotic Diseases
Min-Qi Jia, Cha-Xiang Guan, Jia-Hao Tao, Yong Zhou, Liang-Jun Yan
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease increases the risk of end-stage renal disease in patients with biopsy-confirmed diabetic nephropathy: a propensity-matched cohort study
Yutong Zou, Lijun Zhao, Junlin Zhang, Yiting Wang, Yucheng Wu, Honghong Ren, Tingli Wang, Yuancheng Zhao, Huan Xu, Lin Li, Nanwei Tong, Fang Liu
Acta Diabetologica.2022; 60(2): 225. CrossRef - FGF21 and Chronic Kidney Disease
João Victor Salgado, Miguel Angelo Goes, Natalino Salgado Filho
Metabolism.2021; 118: 154738. CrossRef - The Multiple Roles of Fibroblast Growth Factor in Diabetic Nephropathy
Junyu Deng, Ye Liu, Yiqiu Liu, Wei Li, Xuqiang Nie
Journal of Inflammation Research.2021; Volume 14: 5273. CrossRef - Therapeutic effect and mechanism of combined use of FGF21 and insulin on diabetic nephropathy
Fanrui Meng, Yukai Cao, Mir Hassan Khoso, Kai Kang, Guiping Ren, Wei Xiao, Deshan Li
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics.2021; 713: 109063. CrossRef - FGF19 and FGF21 for the Treatment of NASH—Two Sides of the Same Coin? Differential and Overlapping Effects of FGF19 and FGF21 From Mice to Human
Emma Henriksson, Birgitte Andersen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - FGF21: An Emerging Therapeutic Target for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis and Related Metabolic Diseases
Erik J. Tillman, Tim Rolph
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Fibroblast growth factor 21 alleviates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





